全球利率路径在 2026 年显著分化,Bloomberg Economics 预计美国、欧元区、日本等主要经济体将进入“非同步”政策阶段。美联储当前联邦基金利率上限为 3.75%,预计年底降至 2.75%,较市场仅预测的两次小幅降息更为宽松;相较之下,除去美国后,发达经济体总体利率水平预计全年几乎不变。美国劳动力市场疲软与通胀高企形成拉锯,Bloomberg 预期美联储将在 2026 年降息 100 个基点(1 个百分点),而英国央行预计仅小幅降至 3.5%,欧央行将维持 2% 不变,日本央行则将从 0.75% 升至 1%。
在其他 G7 经济体中,加拿大央行料在 2.25% 附近维持大部分时间,年底可能小幅升至 2.5%;瑞士国家银行将维持 0%,年底或加至 0.25%;挪威央行在 4% 附近逐步下调至 3.5%–3.75%。澳大利亚储备银行预计年底现金利率降至 2.75%,而新西兰储备银行则预期维持 2.25% 或小幅下调。发达经济体普遍进入微调区间,与此同时,地缘政治与特朗普政府的财政与司法干预使政策不确定性加剧,美联储内部独立性面临前所未有的压力。
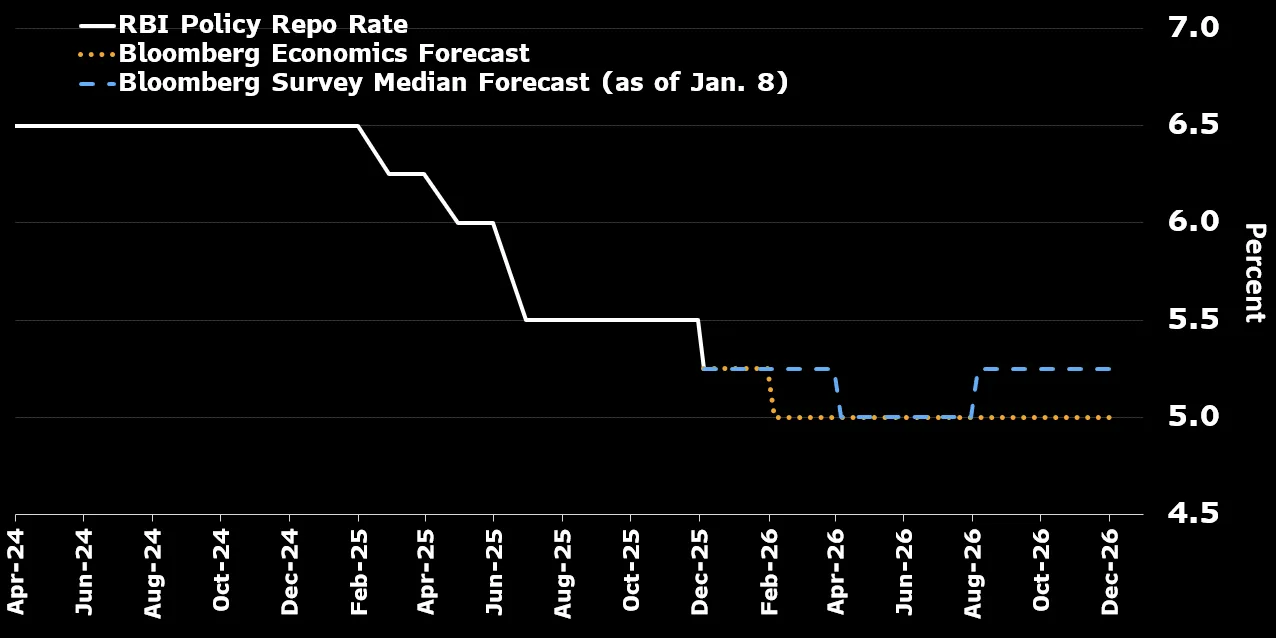
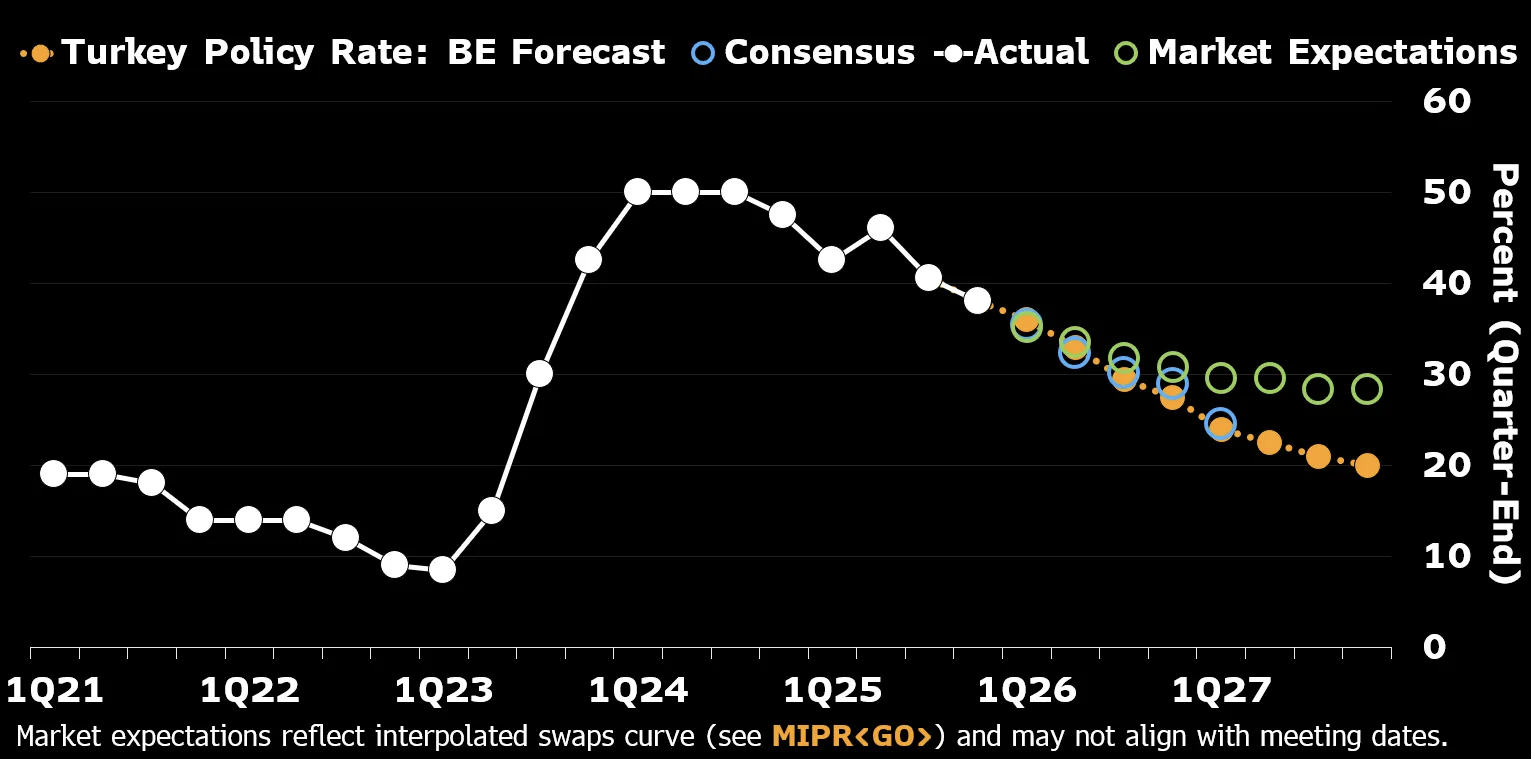
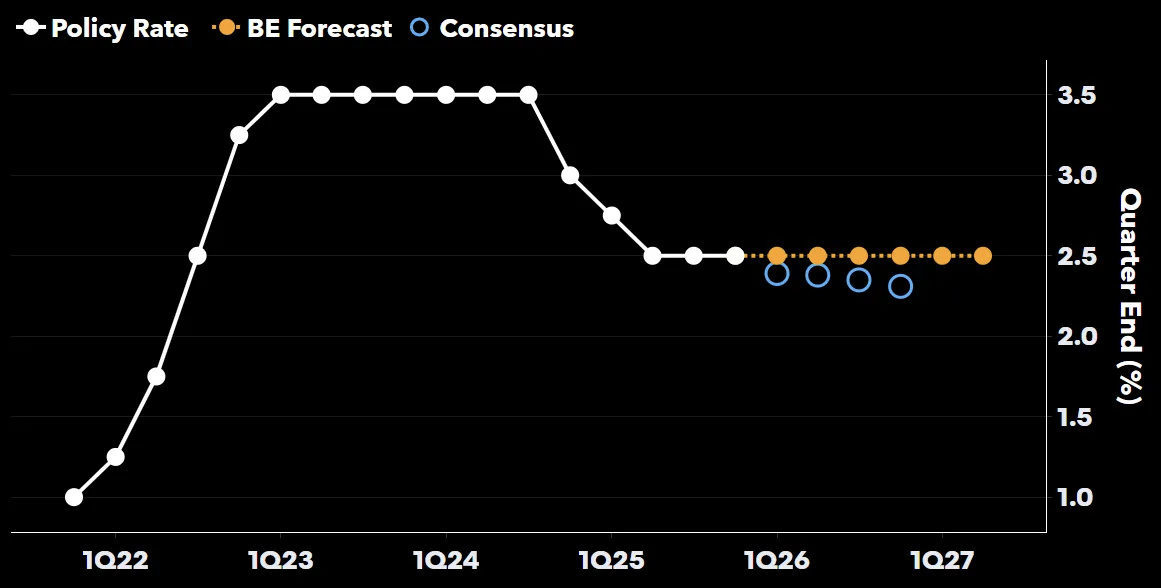
在新兴市场与金砖国家中,中国央行将 7 日逆回购利率由 1.4% 降至 1.2%,印度央行回购利率从 5.25% 调至 5%,巴西塞利克利率由 15% 降至 11%,俄罗斯关键利率由 16% 降至 12%,尼日利亚从 27% 降至 23.5%,印尼从 4.75% 降至 3.75%,土耳其则从 38% 降至 27.5%。总体趋势为美联储深度降息带动新兴市场同步宽松,而发达经济体保持分化:美国宽松、欧洲停滞、日本趋紧。整体政策分歧反映 90% 全球经济体在特朗普二任下的宏观政策重新排序。
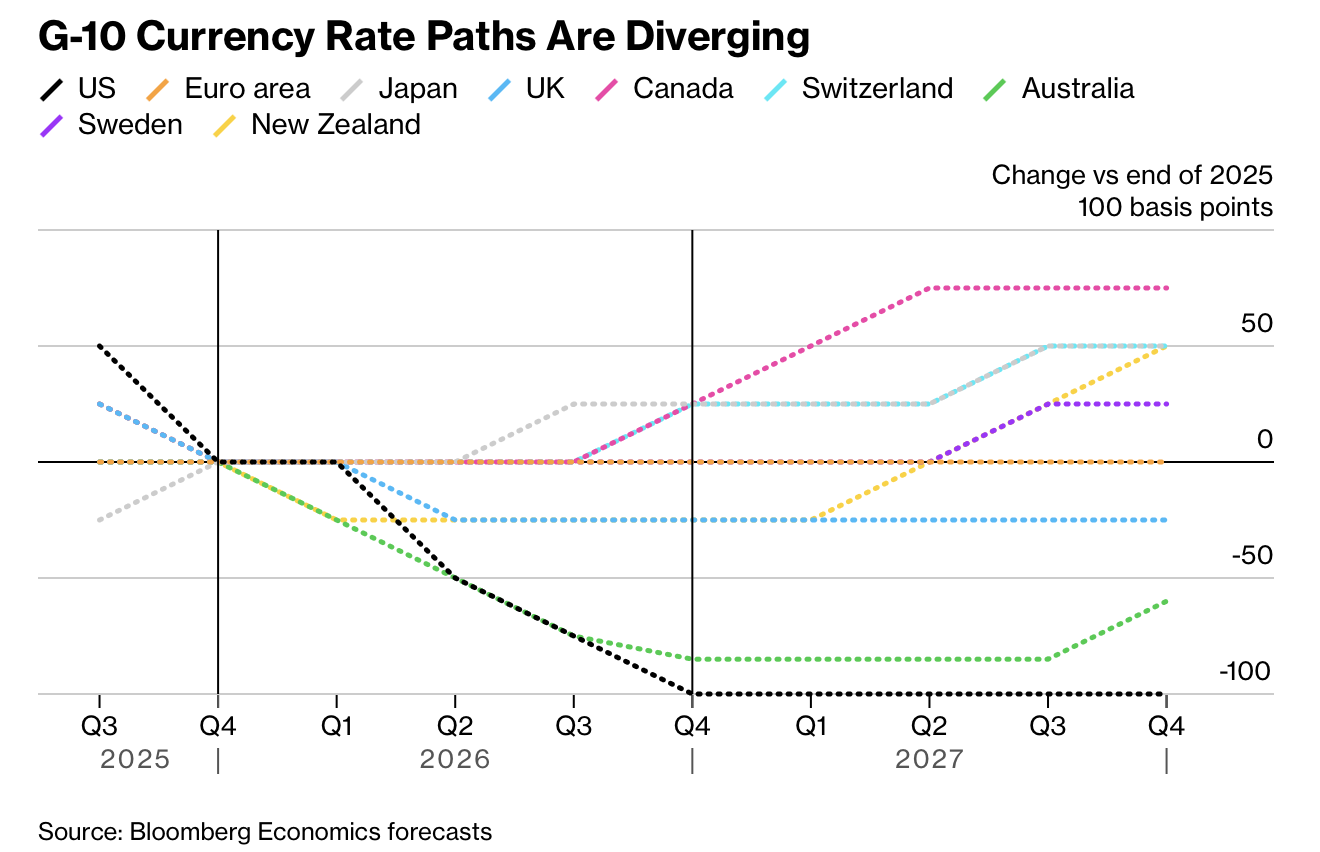
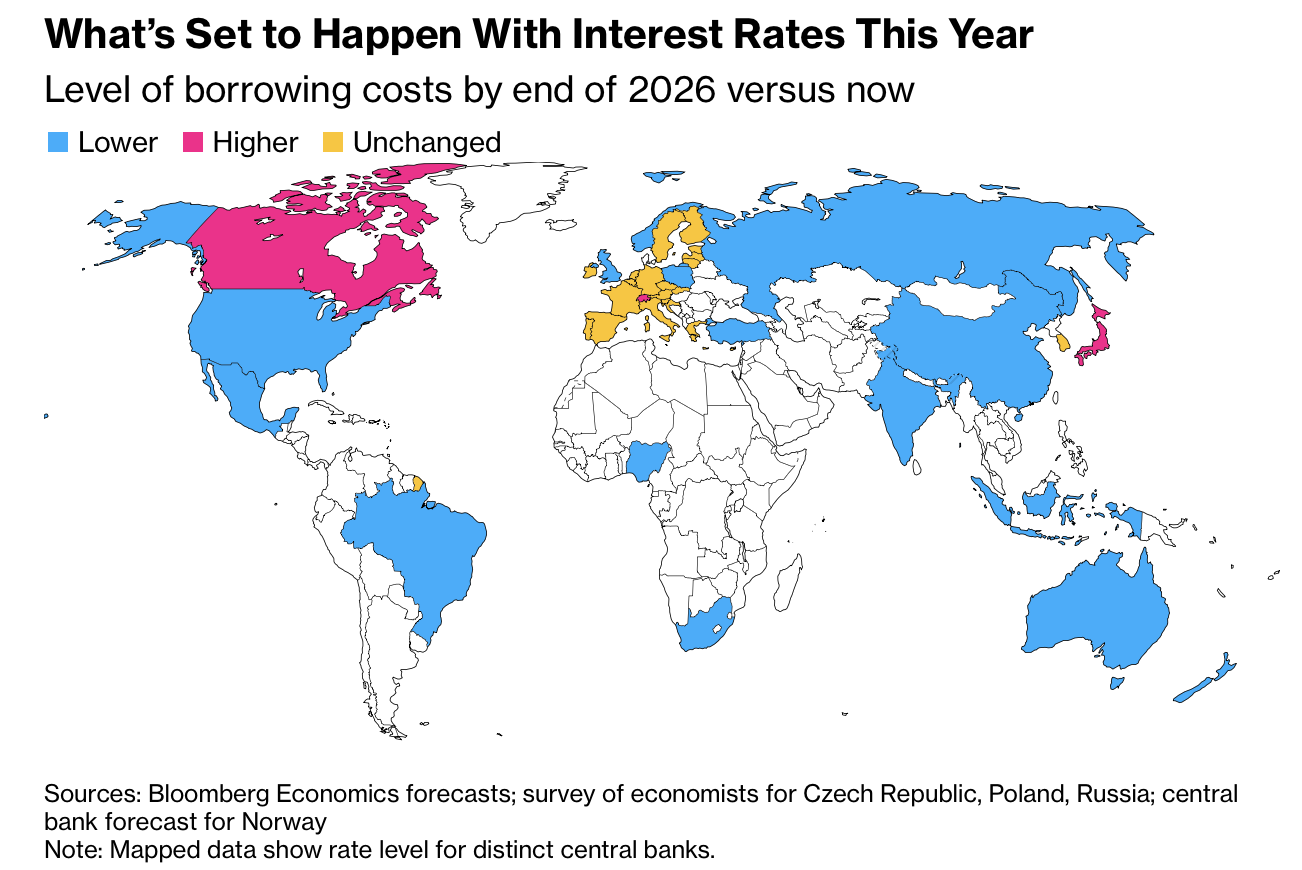
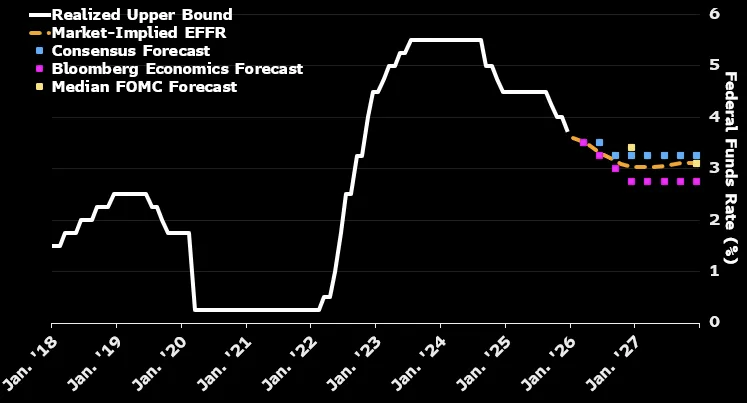
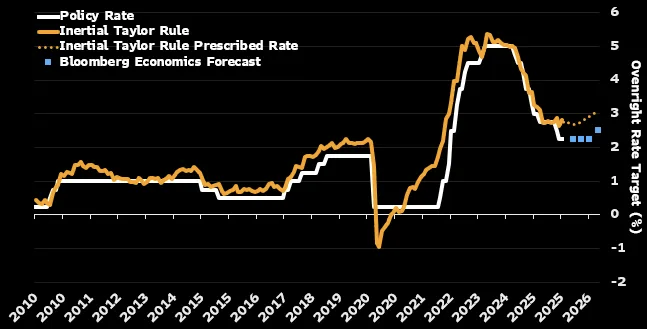
Global interest-rate paths are splintering in 2026, with Bloomberg Economics projecting a “desynchronized” phase across major economies. The US Federal Reserve’s current upper-bound rate of 3.75% is forecast to drop to 2.75% by year-end—more easing than markets’ two-cut expectation—while excluding the US, aggregate advanced-economy rates will remain nearly flat. The US labor market remains weak while inflation stays above target; Bloomberg projects the Fed will cut 100 basis points in 2026. The Bank of England is forecast to trim to 3.5%, the ECB to hold steady at 2%, and the Bank of Japan to hike from 0.75% to 1%.
Among other G7 economies, the Bank of Canada is expected to hold near 2.25% for most of the year before a late rise to 2.5%; the Swiss National Bank will stay at 0% until a potential 0.25% hike by December; and Norges Bank will gradually ease from 4% to between 3.5% and 3.75%. The Reserve Bank of Australia is forecast to end 2026 at 2.75%, and the Reserve Bank of New Zealand around 2.25%. Advanced economies are entering a fine-tuning phase while geopolitics and Trump’s administration pressure add volatility, threatening the Fed’s independence through legal and political strain.
Across emerging and BRICS markets, China’s PBOC will cut the 7-day repo rate from 1.4% to 1.2%; India’s RBI from 5.25% to 5%; Brazil’s Selic from 15% to 11%; Russia’s key rate from 16% to 12%; Nigeria’s benchmark from 27% to 23.5%; Indonesia’s from 4.75% to 3.75%; and Turkey’s from 38% to 27.5%. The overall trend shows deep US rate cuts leading global easing in emerging markets while advanced economies diverge—US easing, Europe holding, Japan tightening. Together, these shifts redefine monetary alignment across 90% of global GDP under Trump’s second term.