甲骨文信用风险指标在 2025 年 12 月初飙升至自 2009 年 3 月以来最高水平,反映市场对 AI 投资泡沫的担忧。其信用违约互换(CDS)保护成本升至约每年 1.28 个百分点,较前一日增加近 0.03 个百分点,并较 6 月的 0.36 个百分点水平上涨逾三倍。摩根士丹利警告 CDS 可能逼近 2 个百分点、超过 2008 年纪录。推动恐慌的主因包括甲骨文在数月内直接或间接发行数百亿美元债券,以及其信用评级弱于其他云计算巨头,使其 CDS 成为市场对 AI 崩盘进行对冲的主要工具。
截至 2025 年 8 月底,甲骨文总债务约 1,050 亿美元,其中约 950 亿美元为纳入 Bloomberg US Corporate Index 的美国公司债,使其成为除银行业外指数内最大发行者。今年 9 月,甲骨文发行 180 亿美元高评级债券,并参与规模最大 AI 基础设施融资项目,与 OpenAI 的合作预计将在未来数年带来“数千亿美元”收入预期。CDS 交易激增:截至 11 月 14 日的 7 周内交易量达约 50 亿美元,而去年同期仅略高于 2 亿美元。投资者大量买入对冲工具以防止公司在高杠杆与 AI 投资潮中出现信用恶化。
大盘趋势同样显示债务压力加速。美国投资级债券发行量预计 2026 年达 2.1 万亿美元,较 2025 年超过 1.57 万亿美元进一步上升。TD 预测明年信用利差将从 2025 年的 75–85 基点扩大至 100–110 基点。尽管医疗行业曾展示高杠杆扩张也能维持稳健利差的先例,但花旗指出投资者难以从 AI 繁荣中获得上行,而企业持续扩张 AI 资本开支则可能削弱债务质量,引发供给过量与利差显著走阔。
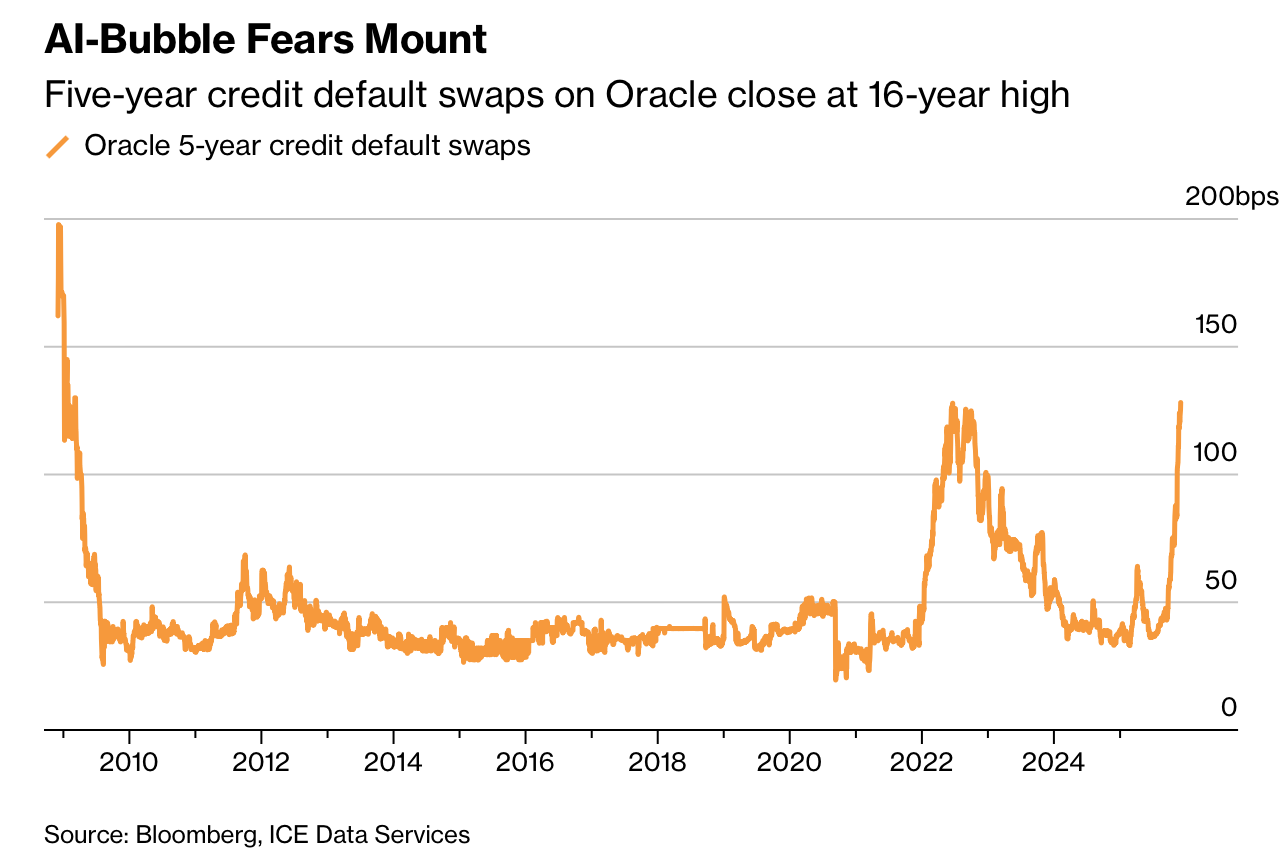
Oracle’s credit-risk gauge surged in early December 2025 to its highest level since March 2009, reflecting rising fears of an AI-driven investment bubble. The cost of credit default swaps rose to about 1.28 percentage points per year—up nearly 0.03 percentage point from the prior day and more than triple the 0.36 percentage point level seen in June. Morgan Stanley warned the CDS spread may approach 2 percentage points, above the firm’s 2008 record. The spike is tied to Oracle’s issuance of tens of billions of dollars in debt—both directly and through AI-related projects—and its weaker credit ratings relative to other cloud hyperscalers, making its CDS a preferred hedge against an AI downturn.
Oracle held roughly $105 billion in debt at the end of August 2025, including about $95 billion in US corporate bonds within the Bloomberg US Corporate Index, making it the largest non-bank issuer in the benchmark. The company sold $18 billion in high-grade bonds in September and is tied to the largest AI-infrastructure financing deal. It expects “hundreds of billions” in future revenue connected to OpenAI. CDS trading ballooned to about $5 billion over the seven weeks ending Nov. 14, compared with just over $200 million in the same period a year earlier, as investors aggressively hedged against potential credit deterioration amid heavy AI-capex leverage.
Broader debt markets show similar strain. US investment-grade issuance is projected to hit a record $2.1 trillion in 2026, up from more than $1.57 trillion in 2025. TD forecasts spreads widening from 75–85 basis points in 2025 to 100–110 next year. While sectors like healthcare have previously endured large debt waves without crisis, Citigroup warns that bondholders capture little upside from an AI boom, and continued AI spending could erode credit quality. Investor hesitation is already pushing sector spreads notably wider.