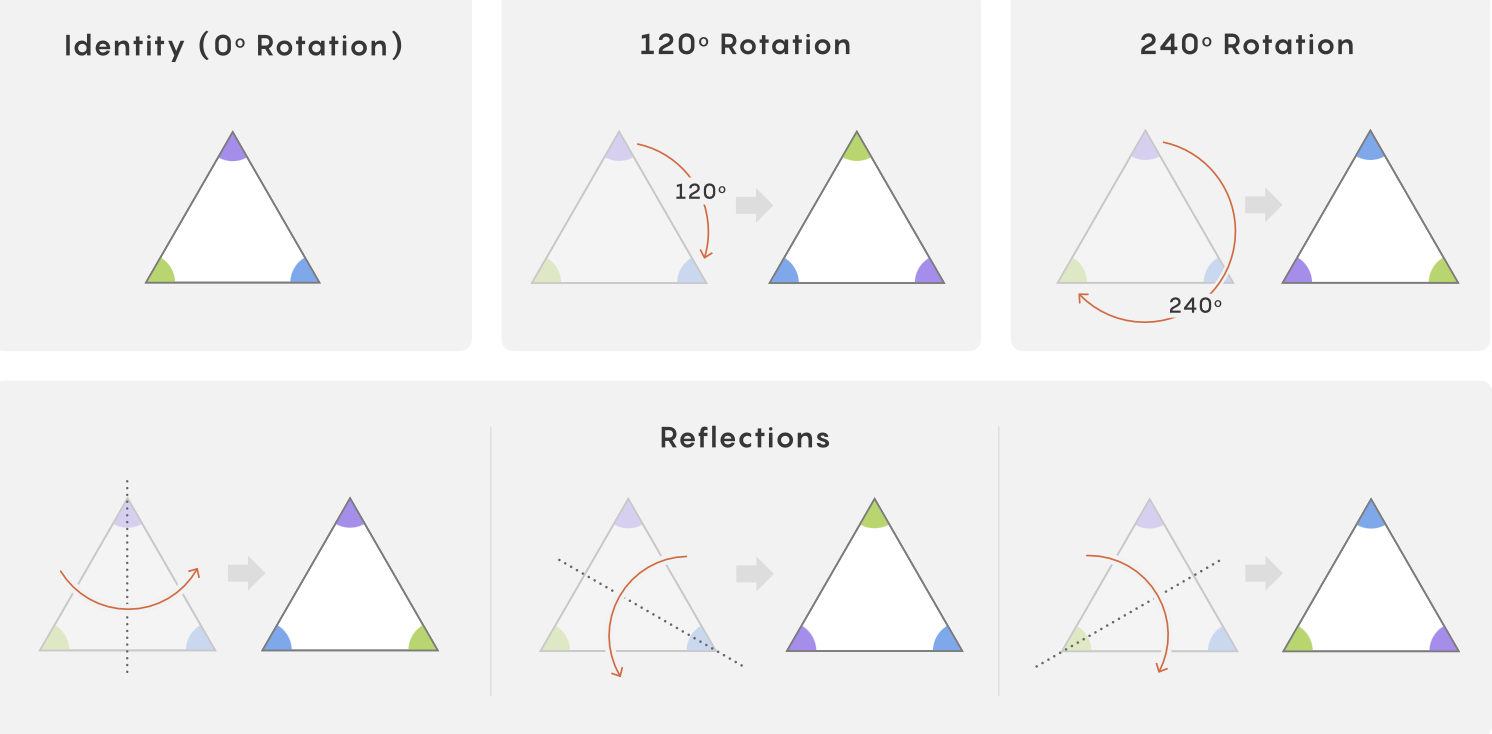
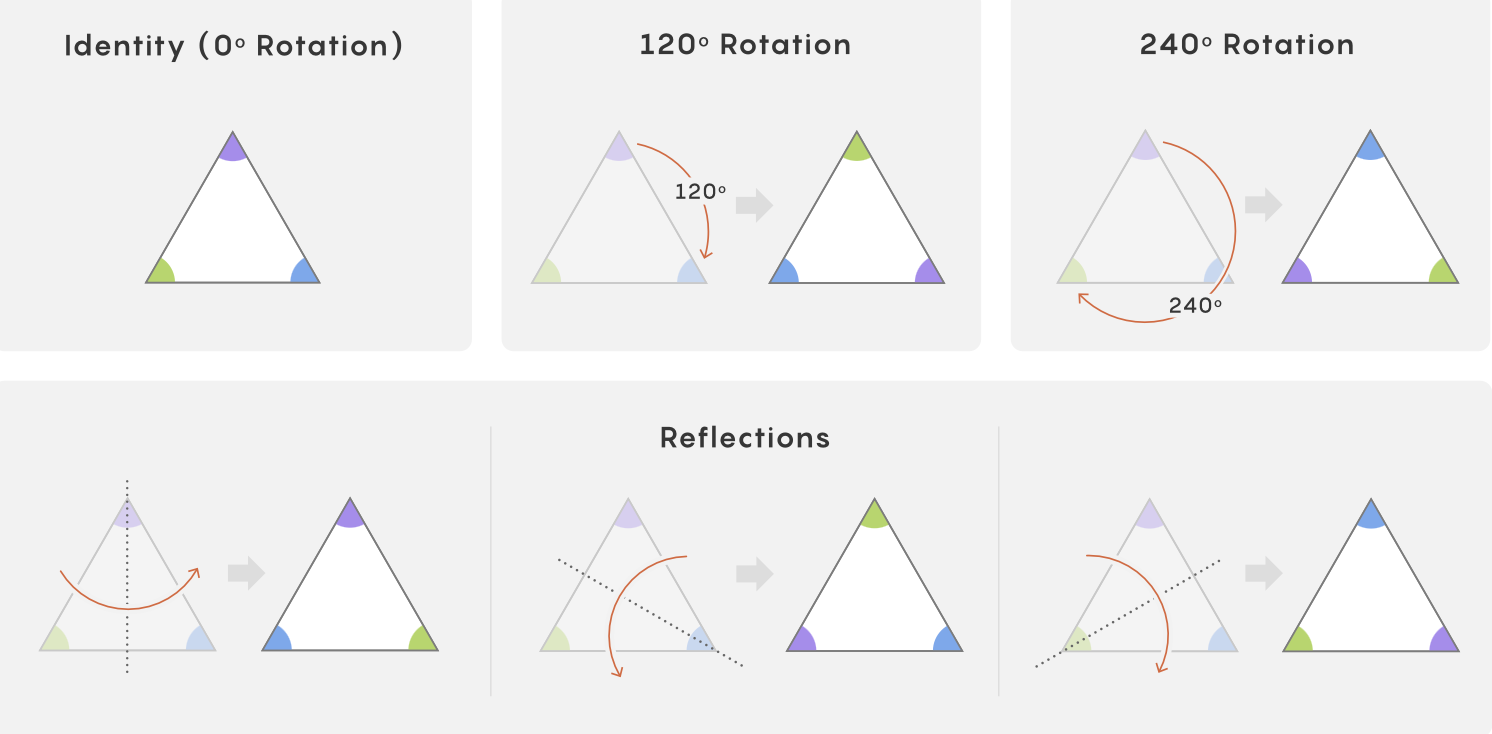
在三角形只有三次离散旋转对称的背景下,圆盘可在任意实数角度下保持外观不变,形成不可数无限多的连续对称,典型例子为 SO(2),其元素在坐标平面中构成一个圆。这种可视为平滑流形的结构定义了 Lie 群,使其具备可微性并可呈现如圆面、球面或更高维度形状,例如 SO(3) 为一个三维流形嵌入九维空间。其流形性质让研究者能使用几何与微积分工具分析群结构,尤其在局部放大时曲率可忽略,使其近似线性。
在 SO(2) 的小角度区域内,曲线近乎直线,使旋转可以切线逼近,此切线即 Lie algebra,包含向量形式的元素以线性化群的核心特性。线性代数工具因此可简化对群的比较与运算,Lie 群与其 Lie algebra 之互动产生广泛结果。该理论源自 Sophus Lie 于 19 世纪后期研究微分方程对称性时的发展,其思想接续自 Évariste Galois 对多项式方程的群论分析,并最终独立成为一门研究连续对称的理论。
自然界的连续对称使 Lie 群在物理中不可或缺。重力在 SO(3) 下不变,基本力皆由 Lie 群对称定义。Emmy Noether 于 1918 年证明每个可由 Lie 群描述的对称都对应一条守恒律,如时间平移对称对应能量守恒。透过此框架,物质结构与基本物理量得以解释,使 Lie 群成为当代数学与物理的核心工具。
 、
、
The triangle admits only three discrete rotational symmetries, whereas a disk remains invariant under any real-valued rotation, producing uncountably many symmetries exemplified by SO(2), whose elements form a circle in the plane. This geometric realization classifies it as a Lie group, a smooth manifold that may resemble circles, spheres, or higher-dimensional structures; SO(3), for instance, is a three-dimensional manifold embedded in nine dimensions. The manifold structure enables the use of geometry and calculus, since local regions become effectively linear when sufficiently magnified.
In small-angle regions of SO(2), curvature becomes negligible, so rotations can be approximated by the tangent line, the Lie algebra, whose vector-like elements linearize the group’s essential behavior. Linear algebra thus streamlines comparison and computation across groups, and the interaction between a Lie group and its algebra yields extensive consequences. The framework originates from Sophus Lie’s late-19th-century analysis of differential-equation symmetries, extending ideas that Évariste Galois had applied to polynomial equations, and ultimately forming a theory of continuous symmetry.
Continuous symmetry in nature makes Lie groups indispensable in physics. Gravity is invariant under SO(3), and all fundamental forces are characterized by Lie group symmetries. In 1918, Emmy Noether proved that every symmetry describable by a Lie group corresponds to a conservation law, such as time-translation symmetry yielding energy conservation. This structure explains properties of matter and fundamental quantities, establishing Lie groups as central tools in modern mathematics and physics.