联合国一份新报告称,世界已进入“全球水资源破产”时代,人类对淡水系统的消耗已超过其恢复能力。全球约四分之三人口,即约61亿人,生活在淡水供应不安全或极不安全的国家,其中40亿人每年至少有一个月面临严重缺水。报告指出,全球淡水取用量持续上升,而多个城市正经历“零日”风险,供水系统接近崩溃。
具体影响已在多地显现。伊朗德黑兰近期的严重缺水促使政府警告可能需要疏散部分城区甚至迁都;土耳其因地下水被过度抽取,已出现约700个塌陷坑,部分深达100英尺。全球一半人口依赖地下水作为生活用水来源,而地下水正在被快速耗尽;另有四分之一人口依赖的大型湖泊自20世纪90年代初以来已流失约一半水量。报告还指出,水量常被高估,因为污染使大量水资源无法使用。
气候变暖提高了用水需求并加剧蒸发,使降水更不稳定,但管理失当是关键放大因素。长期地下水超采、森林破坏、土地退化和污染已在多地造成不可逆的淡水损失。报告呼吁将“水资源破产”纳入政策讨论,建立全球监测框架,并阻止进一步破坏水源的项目。研究还预测,尽管强降雨事件增多,欧洲、北南美和北美西部的农业干旱将加剧,进一步推高灌溉需水量。
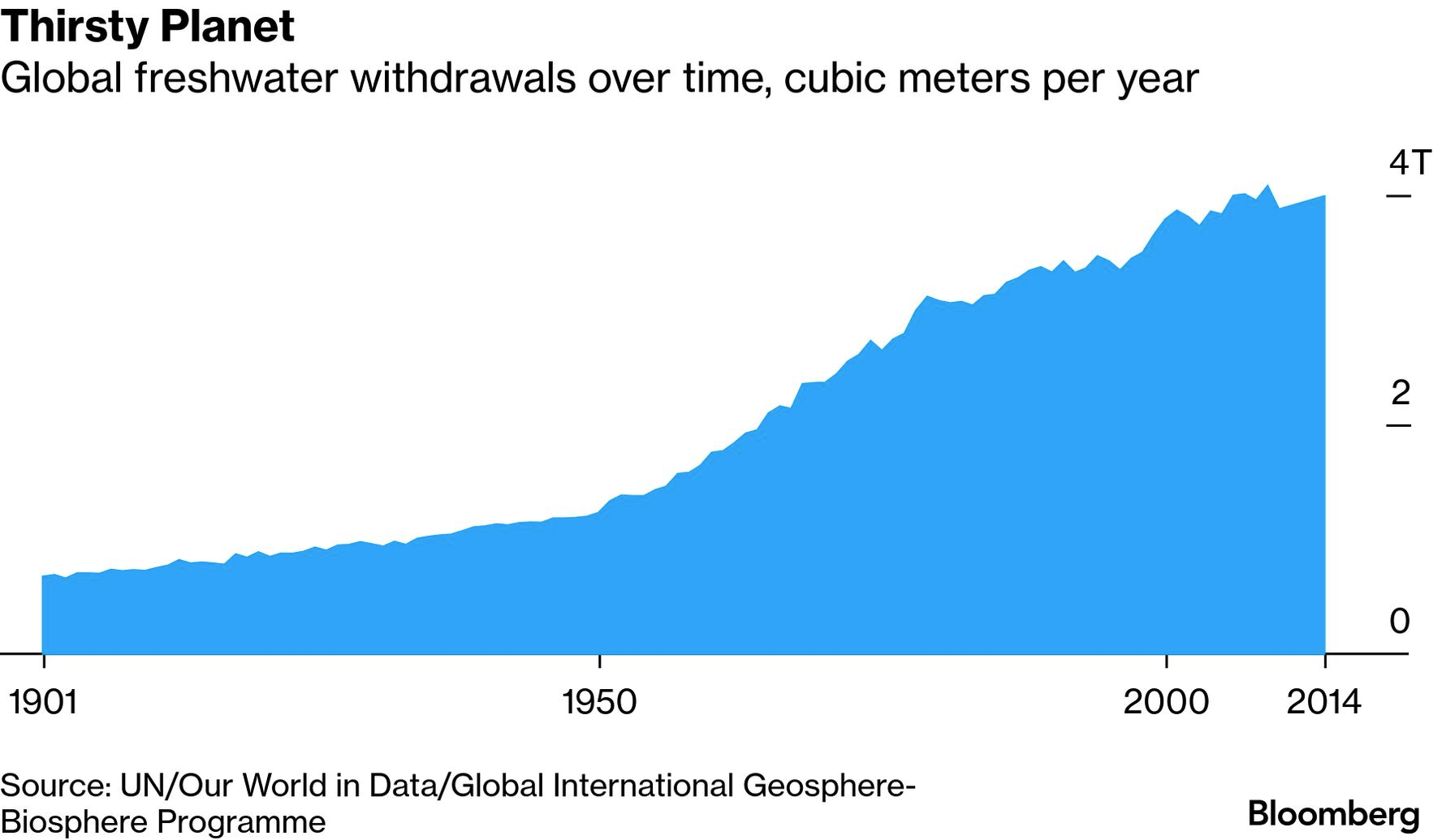
A new United Nations report says the world has entered an era of “global water bankruptcy,” where human depletion of freshwater systems has exceeded their ability to recover. About three quarters of the global population, roughly 6.1 billion people, now live in countries with insecure or critically insecure freshwater supplies, and 4 billion people face severe water scarcity for at least one month each year. Global freshwater withdrawals continue to rise, while more cities face “Day Zero” risks as municipal systems near collapse.
Impacts are already visible. Acute shortages in Tehran prompted warnings that parts of the city may need evacuation or even relocation of the capital. In Turkey, about 700 sinkholes, some up to 100 feet deep, have formed after excessive groundwater extraction. Half of the world relies on stored groundwater for domestic use, which is being rapidly depleted, while a quarter depends on large lakes that have lost about half their volume since the early 1990s. Water availability is often overstated because pollution renders large shares unusable.
Rising temperatures increase water demand and evaporation and make supply less predictable, but mismanagement is a critical amplifier. Chronic groundwater overuse, deforestation, land degradation, and pollution have caused irreversible freshwater losses in many regions. The report urges recognition of water bankruptcy in policy debates, creation of a global monitoring framework, and blocking projects that further degrade supplies. Additional research predicts worsening crop droughts in Europe, northern South America, and western North America despite heavier rain events, further increasing irrigation demand.