西方跨国公司——海外销售额占比超过30%的企业——约占全球上市股票市值的70%,年利润约2.4万亿美元,雇用约1亿人,并贡献全球出口的约三分之二。全球贸易在2001年升至全球GDP的49%(十年前为38%),外国直接投资在2007年达到峰值3万亿美元,即GDP的5.3%。
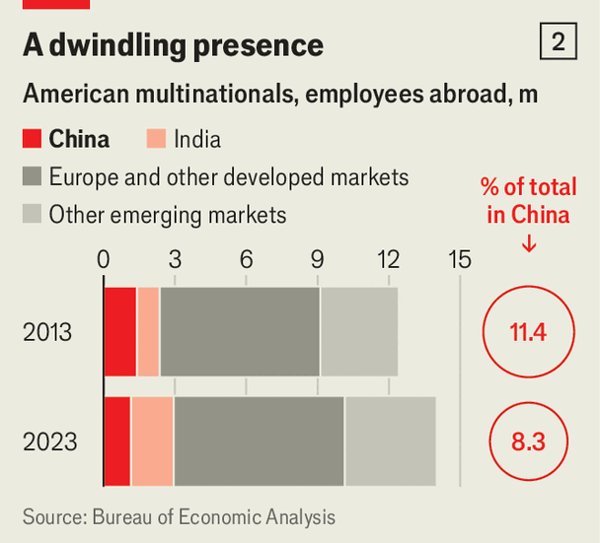
美国跨国公司已转向本土:本土资本开支占比从44%(2016年)升至69%(2025年),截至2023年的五年里海外子公司销售额按实际口径下降1%而国内销售额上升8%,美国境内员工占比从67%小幅升至68%。欧洲也转向美国:美国境内员工在2018–23年增长8%至300万人,赴美FDI存量在2018–24年从2.8万亿美元增至3.6万亿美元,绿地FDI占比从12%升至17%,收入占比从16%升至20%,同时中国在绿地对外投资流出中的占比下降(美国7%→2%,欧洲5%→3%),西方企业在华雇佣在2019–23年减少近十分之一。
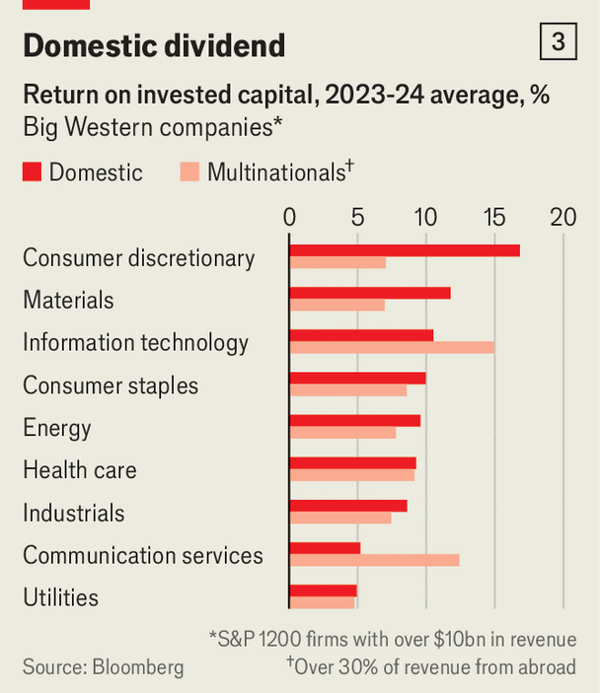
在战略行业中回撤更明显:美国跨国公司在2019至2023年的中位数变化为在华员工-15%、销售-12%、资产-7%;欧洲与芯片相关的对华投资在2021至2023年平均下降46%;战略行业的风险投资流向中国初创企业的份额从4%(2017–19年)滑落至几乎为零。与此同时,战略行业在全球FDI中的占比从2015年的11%跃升至2025年的38%,但敞口仍高(半导体在2024年来自中国的销售额约1740亿美元,约占总额的30%,而标普1200成分股的平均值为6%),重复建设在增加(26%计划为中国单独设立供应链,且台积电估算在台湾以外建厂成本高出4–5倍),盈利能力也在落后(跨国公司在9个行业中的7个落后于本土同行,且本土领先在9个行业中的6个自2018–19年以来扩大)。

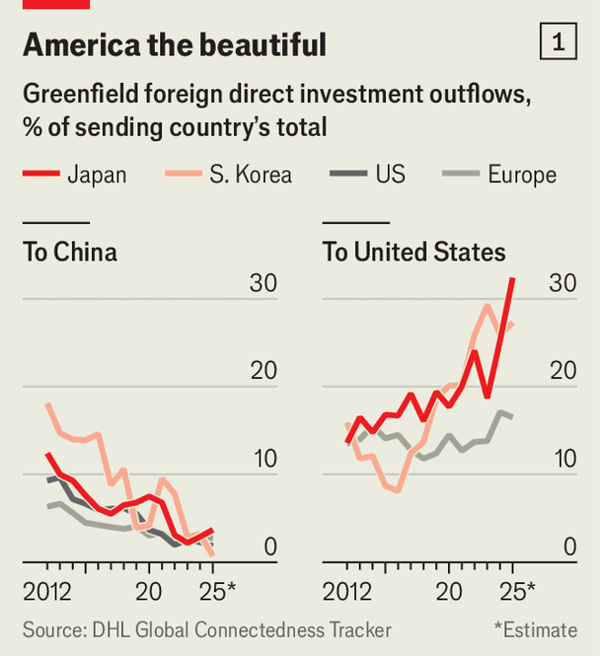
Looking at China, greenfield outflows to the US decreased from 7% to 2%, while employment saw a nearly 10% cut from 2019 to 2023. GDP growth projections show the US averaging 2.6% and China at 5.1%.
Strategic industries are facing challenges, with median staff, sales, and asset drops. European chip manufacturers experienced massive investment reductions, and there is a notable shift in supply chain plans, with 26% aiming for separation.
Now, the focus seems to be shifting toward the US, with American capital expenditures at home rising from 44% in 2016 to 69% by 2025. Foreign sales have seen a real decline of 1%, while domestic sales increased by 8% up to 2023. The employee share has grown slightly from 67% to 68%.
Source: Geopolitics is warping multinationals’ commercial decisions
Subtitle: Firms are reshaping their operations, at the expense of their profits
Dateline: 1月 15, 2026 05:52 上午